Contents
Client Confidentiality for law firms is the foundation of professional credibility. In this blog, we will go over the core principles governing confidentiality obligations, including key regulations in the U.S. and Canada, and discover practical strategies for safeguarding sensitive client information. We’ll also explore common threats—ranging from cyberattacks to human error—and provide actionable tips for implementing robust security measures. By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with best practices to uphold privacy standards, maintain client trust, and protect your firm’s reputation.
Understanding Client Confidentiality
Client confidentiality for law firms is a core legal and ethical duty, requiring firms to protect sensitive information across all communications. This section explores the principles of confidentiality and the key regulations governing it in the U.S. and Canada.
Definition
Client confidentiality for law firms is the ethical and legal obligation to protect all information related to client representation. It extends beyond attorney-client privilege and applies to all forms of communication, documentation, and case details—whether shared intentionally or unintentionally. Lawyers cannot disclose client information without explicit permission, except in rare cases where disclosure is legally required, such as preventing imminent harm or complying with a court order. This duty covers case discussions, emails, texts, digital communications, physical and electronic records, billing details, and third-party disclosures involving staff, vendors, or co-counsel.
Importantly, confidentiality obligations continue indefinitely, even after a case is closed or a client relationship ends.
Legal and Ethical Obligations
Law firms must adhere to strict client confidentiality rules set by professional bodies such as the American Bar Association (ABA) in the U.S. and the Federation of Law Societies of Canada (FLSC) in Canada.
These guidelines govern:
- Attorney-client privilege: lawyers are bound to protect communication between themselves and clients.
- Duty of confidentiality: Preventing unauthorized disclosure of client information.
- Data protection laws: Compliance with regulations such as:
-
- Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) (Canada) – Governs how private-sector organizations handle personal information.
- Provincial privacy laws (e.g., British Columbia’s PIPA, Alberta’s PIPA, and Québec’s Law 25) – Specific to certain jurisdictions in Canada.
- GDPR (EU) and U.S. privacy laws, where applicable for international clients.
- American Bar Association (ABA) Model Rule 1.6 – Prohibits lawyers from revealing client information without informed consent.
- State Bar Association Rules – Each U.S. state has variations of confidentiality regulations that lawyers must follow.
- HIPAA Compliance (For Firms Handling Medical Cases) – Requires strict security measures when managing client health records in personal injury, medical malpractice, or disability cases.
- GDPR & Data Protection Laws (For International Clients)—Firms dealing with EU-based clients must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) data security mandates.
Ensure all attorneys and staff receive ongoing training on confidentiality laws and firm-specific security policies.
Common Threats to Client Confidentiality
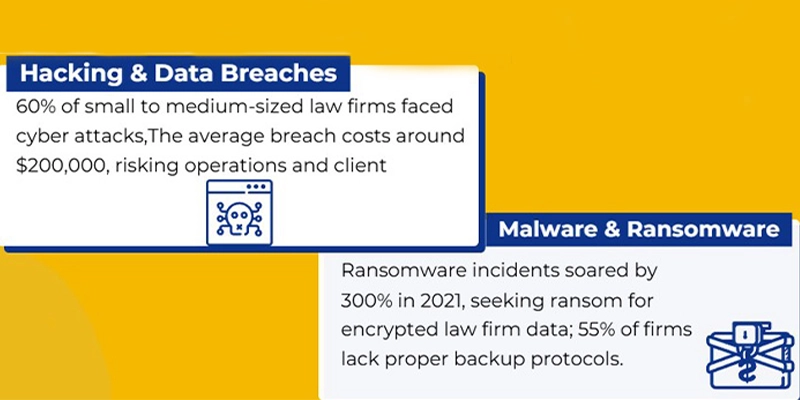
Even with strict legal and ethical safeguards, client confidentiality for law firms remains vulnerable and subject to various threats. Law firms face increasing risks to client confidentiality, ranging from cyber threats to human errors and physical security breaches. Even a single lapse can compromise sensitive client data, violate ethical obligations, and expose firms to legal liability. Understanding these threats is the first step toward implementing stronger security measures.
Cybersecurity Risks
Law firms are prime targets for cyberattacks, and digital security breaches are among the biggest threats to client confidentiality. Hackers exploit weaknesses in email security, unsecured networks, and outdated systems to steal client information.
Human Error
Even simple mistakes can compromise even the most secure systems. Human errors continue to be one of the leading causes of confidentiality breaches in law firms.
Common mistakes include:
- Accidental Email Disclosures – Sending client-sensitive documents to the wrong recipient.
- Misplaced Documents – Leaving case files unattended in public areas, courtrooms, or shared workspaces.
- Verbal Disclosures –Discuss client details in hallways, restaurants, or other non-secure locations where others can overhear.
To minimize human errors, use email encryption tools, enforce strict document handling policies, and conduct regular staff training.
Physical Security Lapses
While digital threats are a major concern, physical security breaches also threaten client confidentiality. Unauthorized individuals gaining access to law offices, case files, or work devices can result in data theft or exposure.
Common physical security risks include:
- Unsecured Offices & File Cabinets – Exposing sensitive case files in open workspaces.
- Unattended Laptops & Mobile Devices – Failing to lock screens or encrypt hard drives, allowing unauthorized access if devices are lost or stolen.
- Unauthorized Office Access – Former employees, cleaning crews, or visitors accessing confidential files or legal correspondence.
Enforce access control policies, install security systems, and require staff to lock up files and devices when not in use.
Best Practices for Safeguarding Client Information
Law firms must proactively protect client data from cyber threats, human error, and unauthorized access. Implementing strong security measures ensures compliance with legal and ethical obligations and safeguards client trust. Here’s how law firms can enhance confidentiality protections.
Implement Robust Cybersecurity Measures
A law firm’s digital security framework must be strong enough to prevent data breaches, hacking attempts, and unauthorized access. The American Bar Association (ABA) emphasizes the importance of lawyers adopting secure technology to protect client data.
Key cybersecurity protections include:
- Encryption – Encrypt all emails, case files, and communications to prevent unauthorized interception.
- Firewalls & Antivirus Software – Deploy firewalls and real-time threat detection to guard against malware and hacking attempts.
- Secure File-Sharing Platforms—Use platforms like TitanFile or with encrypted client portals to send and receive confidential documents safely.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Require multiple verification steps for access to case management systems and legal documents.
Set up automatic security updates on all firm devices to prevent vulnerabilities from outdated software.
Establish Clear Policies and Procedures
Regardless of size, every law firm must maintain clear, written policies that specify how the firm collects, stores, and shares client data. Following the American Bar Association (ABA) recommendations, law firms should frequently update and communicate protective protocols to each staff member to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats and ethical standards.
Below are key areas to address when developing or refining your firm’s data security protocols:
Data Handling Guidelines
Define which information your firm deems confidential and clarify how staff should store each data type. Include steps for categorizing documents by sensitivity and implementing protocols for access control.
File Retention & Destruction Policies
Establish precise retention schedules for client files and keep them for the legally required duration. A secure disposal method—physical shredding or digital wiping—should also be used to prevent the unauthorized recovery of sensitive information.
Email & Communication Protocols
Create firm-wide rules for handling sensitive emails, including guidelines on when to use encryption. Address the use of personal devices and remind employees to exercise caution when discussing client matters outside the office or on unsecured communication channels.
Third-Party Vendor Compliance
All external service providers—such as cloud storage, transcription, or IT support—must follow your firm’s confidentiality and data security standards. Include contractual provisions and conduct regular vendor assessments to mitigate risks.
Employees must review and acknowledge these data security policies at least once a year. This routine check clarifies responsibilities and encourages vigilance when safeguarding client information.
Conduct Regular Training for Better Security
Even the most advanced security systems can fail when human error occurs. Many breaches stem from staff members who lack awareness of potential risks or overlook essential security protocols. By investing in regular training, firms can close these knowledge gaps and empower employees to protect confidential information more effectively. Key Training Areas:
Recognizing Cyber Threats
Show employees how to identify phishing scams, suspicious links, and possible hacking attempts. Building a heightened vigilance helps your team stay one step ahead of cybercriminals.
Safe Document Handling
Train staff on the proper handling of sensitive documents, emphasizing best practices for secure storage, password protection, and enforcing strict role-based access controls
Client Communication Best Practices
Reinforce the firm’s approved methods for sending emails, making phone calls, and sharing files. Proper communication protocols can significantly reduce data leakage risks.
Schedule mandatory cybersecurity training every six months and conduct spontaneous internal audits to verify compliance. It will ensure that your team remains informed and accountable.
Restrict Access to Sensitive Information
Securing Legal Documents Through Proper Access Control
Limiting who can view and manage sensitive legal documents is part of any law firm’s security strategy. Not every staff member needs unfettered access to every piece of legal information, and restricting permissions to only those who require them to perform their jobs significantly reduces the risk of internal breaches. According to Safety Net—a security firm specializing in legal data protection—implementing strict access control policies is one of the most reliable ways to safeguard sensitive case files from unauthorized handling.
Role-Based Permissions
A practical way to strengthen document security is to align access privileges with each team member’s responsibilities. For example, only attorneys and specific authorized staff should handle client-sensitive information. By following this “need-to-know” principle, a firm minimizes unnecessary exposure of confidential data.
Password-Protected Case Files
Requiring unique, strong passwords for every case file or secure database login ensures that gaining unauthorized entry becomes more difficult. This protection layer helps keep client records safe, even if one set of credentials is compromised.
Physical Security for Printed Files
Although many focus on digital security, law firms must protect physical documents. Locking paper case files in secure cabinets or restricted office areas helps keep critical information safe and preserves client trust.
Actionable Tip
A simple yet powerful practice to consider is using audit logs to track who accesses which files and when. Monitoring file activity creates a culture of accountability, as team members remain aware that their access—especially for high-profile or sensitive documents—is being recorded. By routinely reviewing these logs, firms can spot suspicious behavior early and address issues before they escalate into serious breaches.
Developing a Robust Incident Response Plan
Even with robust security measures in place, data breaches can still happen. A well-defined incident response plan ensures that your law firm reacts quickly and effectively to limit potential damage. Based on Safety Net’s research, a security firm specializing in legal data protection, every firm should establish clear, structured protocols for dealing with breaches to protect both client interests and the firm’s reputation.
Key Elements of an Incident Response Plan
- Immediate Threat Assessment: Identify and contain the breach’s origin quickly to prevent further damage.
- Client Notification Procedures: Meet legal obligations by informing affected clients promptly and transparently.
- Internal Investigation & Documentation: Record the incident, analyze vulnerabilities, and implement corrective measures.
- System Updates & Future Prevention: Patch security gaps and adopt stronger safeguards to reduce the likelihood of a repeat incident.
Conduct annual security drills that simulate a potential data breach. These drills help your team practice their response strategies and refine the plan to ensure readiness if an actual breach occurs.
Leveraging Technology to Enhance Confidentiality
As cyber threats and data breaches get more advanced, law firms must integrate technology-driven solutions to enhance client confidentiality. Secure communication, encrypted document storage, and automated data management systems help minimize risks, ensure compliance, and improve efficiency. Here’s how legal professionals can leverage technology to safeguard client data.
Secure Communication Tools
Relying on standard email, phone calls, or messaging apps risks client confidentiality. Unwanted parties can intercept regular non-secured channels or lead to unintended data leaks. As highlighted in TitanFile’s best practices for client confidentiality, law firms should adopt specialized, encrypted communication platforms to safeguard sensitive information. By choosing the right tools and training staff to handle data correctly, firms can avoid breaches and preserve client trust. Key Features of a Secure Communication Platform:
End-to-End Encryption
Ensures only authorized recipients can read messages or access shared documents.
Secure File Transfer
Secure file transfer ensures that confidential case files remain protected from unauthorized access during transmission, typically by using robust encryption and strict access controls.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Adds a critical security layer beyond a single password, reducing the risk of account compromise.
Use of Disclaimers
Including confidentiality statements—particularly in emails—serves as a legal safeguard, reminding recipients of the sensitive nature of the information.
Even the most advanced tools fall short if you don’t train your staff effectively. Lead workshops on encryption best practices, secure login procedures, and properly handling confidential data. This proactive strategy reduces the risk of accidental disclosures and fortifies overall data security across your firm.
Centralizing Operations with Practice Management Software
Managing client information, case files, and legal correspondence across multiple platforms can increase the risk of data breaches, human error, and compliance failures. Practice management software solves these challenges by centralizing case data, improving access control, and automating key security measures.
- Secure Cloud Storage: Eliminating the risk of physical file theft or unauthorized access through secure storage.
- Role-Based Access Control: Only authorized personnel can view or modify sensitive case files.
- Automated Compliance Tracking: Keeps client confidentiality policies updated and enforced.
RunSensible is a comprehensive practice management platform that offers secure client data storage, automated document handling, and encrypted communication tools. By integrating these features into one solution, your firm can reduce the complexity of managing critical information while boosting overall security.
Implement access logs and audit trails within your practice management system to track who accesses client files and when. This simple yet effective step provides clear visibility into file interactions and helps maintain accountability across your team.
Regular System Backups
Data loss from cyberattacks, accidental deletions, or hardware failures can damage client trust and disrupt legal operations. Routine backups help protect critical case files and client communications, ensuring they remain intact and easily retrievable in emergencies.
Best Practices for System Backups
- Automated Cloud Backups
Schedule real-time or daily backups to minimize the risk of data loss.
- Offsite Backup Storage
Store encrypted copies in multiple, secure locations to protect against onsite disasters or breaches.
- Disaster Recovery Plans
Develop protocols for restoring lost or compromised data and reducing downtime during critical incidents.
Conduct quarterly data recovery drills to confirm your firm’s ability to quickly restore vital documents in a crisis. This proactive approach helps maintain operational continuity and client confidence.
Legal Implications of Breaches in Confidentiality
A breach of client confidentiality can have serious consequences for a law firm, ranging from disciplinary actions and lawsuits to permanent reputational damage. Law firms that fail to protect client information violate ethical and legal obligations and risk losing client trust and business credibility. Here’s what’s at stake when a confidentiality breach occurs.
Professional Disciplinary Actions
Client confidentiality is a fundamental duty in the legal profession, and violations can result in severe disciplinary actions from bar associations and regulatory bodies. Attorneys who fail to protect client information may face ethics investigations, fines, license suspension, or disbarment. Law firms can also be penalized for inadequate security measures. Corrective actions such as mandatory training, compliance monitoring, or security upgrades are often required.
Case Example: In 2019, the State Bar of California publicly reprimanded an attorney for accidentally exposing confidential client emails. The bar required the attorney to complete ethics and cybersecurity training to prevent future breaches.
To avoid disciplinary consequences, attorneys should regularly review bar association guidelines and implement mandatory confidentiality training for all firm employees. Proactively securing client data helps protect legal professionals and their clients while maintaining the profession’s integrity.
Legal Liability
Protecting client confidentiality is a legal necessity. When law firms fail to safeguard sensitive information, they risk civil lawsuits and significant financial liability. The firm could face serious legal consequences if a data breach, unauthorized disclosure, or cyberattack harms a client financially or reputationally.
Legal Risks for Law Firms:
- Negligence Lawsuits – Clients can sue firms for damages if their private information is improperly disclosed or exposed.
- Breach of Fiduciary Duty—Attorneys must act in their client’s best interests. Failing to protect confidential data can lead to litigation.
- HIPAA Violations (For Health-Related Cases) – Law firms handling medical malpractice or personal injury cases must comply with HIPAA privacy regulations. A data breach can result in federal fines and potential lawsuits.
- Class Action Lawsuits – If a law firm experiences a large-scale data breach, multiple affected clients may file a Class Action lawsuit, amplifying financial and reputational damage.
Case Example: In 2021, a personal injury law firm faced a multi-million-dollar lawsuit after a cyberattack exposed confidential settlement agreements. The court held the firm accountable for failing to implement proper cybersecurity measures, resulting in severe financial and legal consequences.
Cyber liability insurance can help mitigate financial losses from lawsuits or data breaches. Additionally, law firms should proactively enhance cybersecurity protocols and conduct regular risk assessments to prevent violations before they occur. Protecting client data is not just about compliance—it’s about securing trust and safeguarding your firm’s future.
Reputational Damage
A confidentiality breach can significantly damage a law firm’s credibility, eroding client trust and driving business away. Clients expect their attorneys to protect sensitive information, and any failure in data security can make them seek other firms.
A breach can significantly impact a law firm’s ability to retain and attract clients. Clients are less likely to work with a firm with a history of mishandling private information, and potential clients may turn to competitors with stronger security measures. Adverse media exposure can further amplify the damage, as high-profile breaches often make headlines, harming public perception. Within the legal community, a data breach can raise ethical concerns, making other attorneys hesitant to collaborate or refer clients to the firm.
Law firms should invest in crisis management and public relations strategies to minimize the damage after a security incident. Proactively addressing the breach, reinforcing cybersecurity measures, and reassuring clients can help rebuild trust and protect the firm’s long-term reputation.
Case Studies: Lessons Learned from Confidentiality Breaches
Confidentiality breaches can lead to severe financial, legal, and reputational consequences for law firms. Examining real-world incidents provides insight into common vulnerabilities and firms’ corrective measures to prevent future breaches. Here are three notable cases that highlight the risks and the lessons learned.
Analysis of Real-World Incidents
Law Firm Data Breach Exposes High-Profile Clients (2020)
A global law firm specializing in corporate litigation and mergers suffered a massive data breach, exposing confidential client records, financial agreements, and privileged communications. The cyberattack was executed through a phishing email, where a staff member unknowingly provided login credentials to hackers. Once inside the firm’s network, the attackers exfiltrated thousands of confidential documents, forcing the firm to disclose the breach publicly.
To prevent such breaches, firms must:
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to prevent unauthorized access.
- Conduct firm-wide cybersecurity training to help employees recognize phishing scams.
- Encrypt sensitive documents stored on the firm’s cloud and internal servers.
Following the breach, the firm enforced mandatory security training, strengthened its email filtering systems, and introduced real-time breach detection software to identify suspicious activity before it escalated.
Attorney Discusses Client Case in Public, Leading to Ethical Violation
A high-profile defense attorney was overheard discussing case details during a phone call in a public café by a journalist sitting nearby. The journalist recorded the conversation and published privileged case details, sparking widespread media attention. The breach damaged the client’s legal position and led to the firm facing a formal ethics complaint from the state bar.
This case highlights a critical issue: verbal security is as important as digital security. Many law firms focus on firewalls and encryption but overlook the risks of careless conversations in public spaces. The firm responded by implementing:
- A strict “No Case Discussions in Public” policy.
- Attorneys must use encrypted voice communication apps when discussing confidential matters outside the office.
- Internal confidentiality training emphasizing the dangers of verbal disclosures.
Such incidents remind us that firms must actively enforce confidentiality in both physical and digital environments.
Accidental Email Disclosure Leaks Confidential Client Information (2019)
A law firm representing multiple plaintiffs in a class-action lawsuit mistakenly CC’d opposing counsel and other unintended recipients in an email containing confidential settlement details. The disclosure compromised legal strategy and forced the firm to file a motion to exclude the email from consideration, which the court denied. The firm was sanctioned for failing to uphold basic confidentiality protocols.
This firm could have avoided this breach with the following:
- Email encryption to protect sensitive attachments.
- A delay-send feature that allows attorneys to retract emails before they are delivered.
- A double-check policy requires attorneys to verify recipients before sending legal communications.
After the incident, the firm adopted AI-powered email security tools that detect and prevent misdirected emails before they leave the firm’s network.
Preventative Measures Implemented Post-Breach
Confidentiality breaches often result in financial losses, disciplinary actions, and declining client trust. However, firms that take proactive steps after a breach can rebuild their security framework and prevent similar incidents in the future.
To mitigate risks, many firms have:
- Strengthened cybersecurity protections by upgrading firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encrypted storage.
- Mandated annual confidentiality training for all attorneys and staff.
- Enforced strict internal communication policies, requiring encrypted messaging and VPNs for remote work.
- Developed comprehensive incident response plans, ensuring immediate action if a breach occurs.
A firm’s reputation depends on how well it responds to confidentiality threats. Firms that act swiftly and implement preventative measures can turn a security failure into a learning opportunity, ultimately strengthening their operations and earning back client trust.
Making the Most of Client Confidentiality in Your Practice
Client confidentiality hinges on robust data security, clear firm-wide policies, and vigilant team training. By continually prioritizing these efforts, you protect your clients, reinforce trust, and uphold the integrity of your legal services.
An all-in-one practice management platform like RunSensible can be a game-changer for improving security and boosting efficiency. Its secure cloud storage, encrypted communication tools, and automated backup features seamlessly integrate to help your firm comply with privacy laws and ethical standards. Plus, real-time monitoring and built-in audit trails give you complete visibility into who’s accessing sensitive information and when making it easier to prevent and respond to breaches. When you centralize your operations with RunSensible, you streamline workflows and add protection against cyber threats and human errors.
Ultimately, taking a proactive, technology-driven approach and fostering a culture of accountability ensures that law firms’ client confidentiality remains uncompromised, safeguarding their reputation, clients’ trust, and practice’s future success.
Safeguard your practice with robust security measures and cutting-edge legal technology. Get started with RunSensible to centralize client data, automate secure workflows, and protect the trust you’ve built.
FAQs:
1. What severe penalties to law firms face for confidentiality breaches?
Law firms risk disciplinary actions ranging from fines and license suspensions to disbarment, depending on the severity of the breach. They may also face negligence lawsuits or breach-of-fiduciary-duty claims from clients seeking damages. In large-scale breaches, multiple clients can file a class action lawsuit, significantly amplifying financial and reputational harm. Ultimately, any confidentiality breach undermines client trust and can jeopardize the firm’s standing within the legal community.
2. What are the most common threats to client confidentiality?
Cyberattacks, human errors (like sending an email to the wrong recipient), and physical security lapses (e.g., unsecured file cabinets) are the main threats. Vigilance and proper security measures can help minimize these risks.
3. What key regulations should U.S.-based and Canadian law firms monitor to ensure compliance with client confidentiality obligations?
Firms must follow the American Bar Association (ABA) Model Rules—especially Rule 1.6—and any applicable state bar regulations. In Canada, the Federation of Law Societies of Canada (FLSC) sets the national framework, supplemented by provincial laws like PIPEDA, BC’s PIPA, and Québec’s Law 25. Firms with international clientele may also need to comply with GDPR for EU-based clients.
4. In what ways do court scheduling and remote work arrangements increase confidentiality risks, and how can firms adapt?
Court scheduling systems often involve shared calendars and digital filing portals, creating potential data exposure points. Remote work expands the attack surface through personal devices and unsecured networks. Firms can adapt by implementing VPNs, secure collaboration tools, regular cybersecurity training, and strict device-use policies to maintain robust confidentiality standards.
References:
https://www.interlegal.net/a-guide-to-data-security-for-law-firms/
https://www.safetynet-inc.com/resources/blog/5-strategies-for-enhanced-confidentiality-in-law-firms
https://www.titanfile.com/blog/6-best-practices-for-client-confidentiality/
Disclaimer: The content provided on this blog is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, financial, or professional advice.